Auriculotherapy
(Auricular therapy)
$75 for initial treatment.
$50 for each additional treatment.
Auriculotherapy (auricular therapy, ear acupuncture, and auriculoacupuncture)
is a form of alternative medicine based on the idea that the ear is a microsystem and an external organ, which reflects the entire body, represented on the auricle, the outer portion of the ear.
Conditions affecting the physical, mental, or emotional health of the patient are assumed to be treatable by stimulation of the surface of the ear exclusively. Similar mappings are used by several modalities, including the practices of reflexology and iridology.
French neurologist Paul Nogier invented auriculotherapy in 1957. Nogier developed a phrenological method of projection of a fetal Homunculus on the ear and published what he called the "Vascular Autonomic Signal" which measured a change in the amplitude of the pulse. That mechanism would only produce a signal upon the introduction of new information to the electromagnetic field of the patient. Nogier cited a 'principle of matching resonance' which he could use the vascular autonomic signal to detect the active points of the auricular microsystem.
Nogier's Auricular acupuncture was introduced to China in 1958.
A variation of auriculotherapy called "ear stapling" involves the long-term insertion of a medical staple in the conchal bowl of the ear. Advocates variously claim that the procedure aids in losing weight, stopping smoking, and managing stress.
The principles of auriculotherapy are contrary to known anatomy and physiology of the human body.
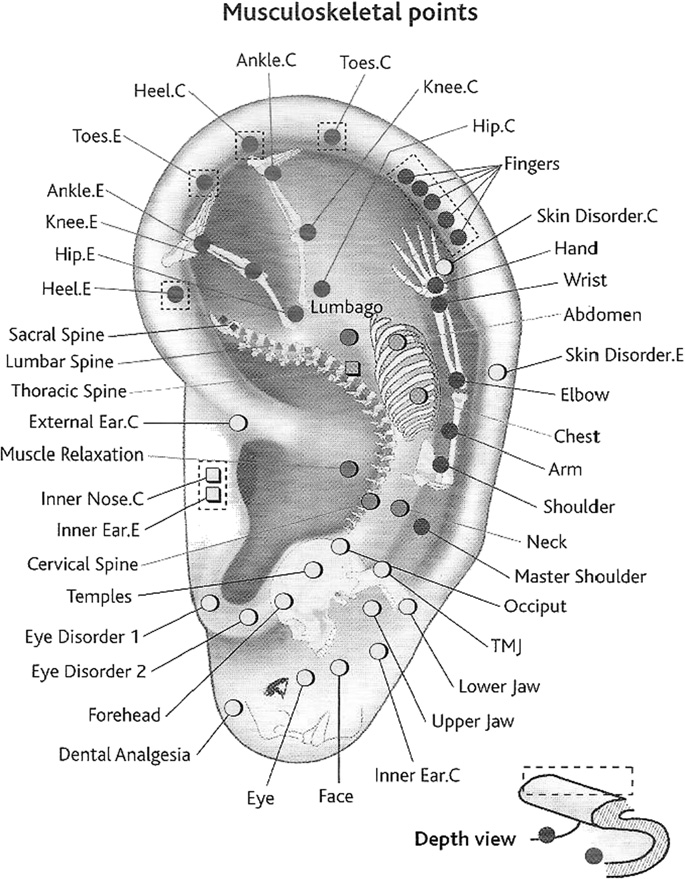
According to Nogier, the relevant structures include:
Helix, the outer prominent rim of the auricle
Antihelix, the elevated ridge anterior and parallel to the helix
Triangular fossa, a triangular depression
Scapha, the narrow curved depression between the helix and the antihelix
Tragus, the small, curved flap in front of the auricle
Antitragus, the small tubercle opposite to the tragus
Concha, the hollow next to the ear canal
Various points located on the ear lobe are related to the head, and facial region, those on the scapha are related to the upper limbs, those on the antihelix and antihelix crura to the trunk and lower limbs and those in the concha are related to the internal organs
HOW AURICULAR WORKS
A key component of all auricular therapy is balancing the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve controls the activity of the autonomic nervous system, which supplies the nerves to the organs, or other parts of our bodies, which work on auto-pilot. A few examples are: the cardiovascular, respiratory, and gastrointestinal systems. The vagus nerve also has an effect on smooth muscles, blood vessels, sweat glands, and the endocrine system.
When the vagus nerve is not functioning properly this can lead to a range of problems throughout the body. These problems can include digestive issues, heart palpitations, improper autoimmune responses, anxiety, depression, and more.
Various issues can affect the vagus nerve and cause it to malfunction, including:
injuries to the head, neck, or chest
chronic stress, inflammation, and nerve damage
conditions such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and cardiovascular disease.
lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and chronic sleep deprivation.
Vagus Nerve Disorders
When the vagus nerve is not working properly, it can cause a variety of nerve disorders:
Gastroparesis: Gastroparesis is a disorder that causes a delay in stomach emptying. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, bloating, and early satiety.
Neurogenic Bladder: A neurogenic bladder can have symptoms including urinary retention, incontinence, and other bladder issues.
Arrhythmia: Damage to the vagus nerve can cause irregular heartbeat, which is also known as an arrhythmia.
Tinnitus: If you have experienced a ringing in your ears on a regular basis, this can also be the result of vagus nerve damage or dysfunction.
Fibromyalgia: This is a very difficult disease to diagnose. Some studies have found that a low vagal tone is indicative of inflammatory diseases like Fibromyalgia and by helping the vagus nerve function properly, there is an anti-inflammatory response to the therapy that can help with the management of pain symptoms. The role of the vagus nerve in fibromyalgia syndrome – PubMed (nih.gov)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): is a catch-all condition characterized by bloating, abdominal pain, and changes in bowel habits.